Biological Classification | Quality Hinglish NEET Notes | Class 11 Biology
Yahan hum detailed complete NEET notes cover karte hain Biology, Chapter Biological Classification, Class 11 Science ke liye.
1. Classification of Living Organisms – Evolution from Ancient to Modern Systems
Shuru se hi human civilization me, log living organisms ko classify karne ki koshish kar rahe the. Initially, ye bina kisi scientific method ke kiya jaata tha. Iske bajay, classification human needs jaise food, shelter, aur clothing ke basis par hoti thi.
Aristotle’s Contribution – First Step Towards Scientific Classification
Pehla vyakti jo zyada scientific classification attempt kiya, wo tha Aristotle.
- Unhone plants ko unke structure (morphology) ke basis par teen groups me classify kiya:
➤ Trees
➤ Shrubs
➤ Herbs - Unhone animals ko bhi do major groups me divide kiya:
➤ Un logo ke saath jinke paas red blood hota hai (jaise vertebrates)
➤ Un logo ke paas red blood nahi hota (jaise invertebrates).
Yeh system simple tha lekin future classification systems ke liye foundation rakhta tha.
Two Kingdom Classification by Linnaeus
Linnaeus ke time par, scientists ne Two Kingdom System propose kiya:
Biological classification samajhna life ki vast diversity ko organize karne ke liye essential hai.
- Kingdom Plantae – isme saare plants plants hain
- Kingdom Animalia – isme saare animals hain
Yeh system neat aur easy lagta tha lekin isme major drawbacks the:
❌ Problems with the Two Kingdom Classification:
- Yeh separate nahi karta tha
- Prokaryotes (jaise bacteria) ko eukaryotes (jaise fungi) se
- Unicellular organisms ko multicellular se
- Photosynthetic organisms (jaise green algae) ko non-photosynthetic (jaise fungi) se
- Bahut se organisms clearly Plantae ya Animalia me fit nahi hote the. For example:
- Fungi – photosynthesis perform nahi karte
- Euglena – plant aur animal dono jaise behave karta hai
Isliye, yeh system time ke saath incomplete aur outdated paya gaya.
Need for Better Classification – Evolving Scientific Approach
Scientists ne realize kiya ki morphology (external appearance) akela enough nahi tha.
Unhe aur bhi kai characteristics consider karni zaroori thi, jaise:
- Cell type (Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic)
- Mode of nutrition (autotrophic or heterotrophic)
- Habitat (aquatic, terrestrial, parasitic)
- Reproduction methods (asexual, sexual)
- Evolutionary relationships
Iske karan, new classification systems develop kiye gaye jo zyada accurate aur detailed the.
Changing Number of Kingdoms Over Time
Jabki Plant aur Animal Kingdoms hamesha kuch form me remain karte rahe, scientists ne samajhna start kiya ki:
- Bahut se organisms kisi bhi kingdom me belong nahi karte.
- Jaise-jaise knowledge badhi, kingdoms ki definition change hui.
- Time ke saath, scientists ne three, four, five, aur even six kingdoms propose kiye taaki life forms ki growing complexity me fit ho sake.
✅ Conclusion
Living organisms ki classification simple, use-based grouping se evolve hokar complex, scientific systems me badal gayi hai. Aaj ke systems sirf organisms ke appearance par based nahi hain, balki is par bhi kiye gaye hain ki woh kis cheez se bante hain, kaise function karte hain, aur kaise evolve hue hain. Classification me yeh evolution hume Earth par life ki vast diversity ko better samajhne me help karta hai.
2. Five Kingdom Classification – R.H. Whittaker’s System
1969 me, R.H. Whittaker ne ek naya, zyada scientific system propose kiya taaki sab living organisms ko classify kiya ja sake. Yeh system Five Kingdom Classification ke naam se jaana jaata hai aur isme shamil hain:
👉 Monera
👉 Protista
👉 Fungi
👉 Plantae
👉 Animalia
🧪 Basis of Whittaker’s Classification
Whittaker ne organisms ko divide karne ke liye scientific criteria use kiye, jaise:
- Cell type (Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic)
- Cell wall composition
- Nuclear membrane (Present or Absent)
- Body organisation (Unicellular, Tissue level, Organ level)
- Mode of nutrition (Autotrophic or Heterotrophic)
- Reproduction and Evolutionary Relationships (Phylogenetics)
🧬 Overview of the Five Kingdoms
Chaliye har kingdom ke key features ko samajhte hain:
🔹 Kingdom Monera
- Cell Type: Prokaryotic
- Cell Wall: Non-cellulosic (made of polysaccharides + amino acids)
- Nuclear Membrane: Absent
- Body Organization: Unicellular (cellular level)
- Nutrition: Both Autotrophic (chemosynthetic & photosynthetic) and Heterotrophic (saprophytic/parasitic)
- Examples: Bacteria, Cyanobacteria
🔹 Kingdom Protista
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic
- Cell Wall: Present in some
- Nuclear Membrane: Present
- Body Organization: Unicellular (cellular level)
- Nutrition: Autotrophic and Heterotrophic
- Examples: Amoeba, Paramoecium, Chlamydomonas, Chlorella
🔹 Kingdom Fungi
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic
- Cell Wall: Present (made of chitin)
- Nuclear Membrane: Present
- Body Organization: Multicellular (loose tissue level)
- Nutrition: Heterotrophic (Saprophytic or Parasitic)
- Examples: Yeast, Moulds, Mushrooms
🔹 Kingdom Plantae
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic
- Cell Wall: Present (made of cellulose)
- Nuclear Membrane: Present
- Body Organization: Tissue/organ level
- Nutrition: Autotrophic (Photosynthetic)
- Examples: Algae, Mosses, Ferns, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
🔹 Kingdom Animalia
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic
- Cell Wall: Absent
- Nuclear Membrane: Present
- Body Organization: Tissue/organ/organ system level
- Nutrition: Heterotrophic (mainly holozoic, some saprophytic)
- Examples: Humans, Insects, Fish, Birds, Mammals
❗ Earlier Classification Systems ke Problems
Whittaker ke system se pehle:
- Saare organisms jinme cell walls the, unhe Plants ke under group kiya gaya, including:
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
- Fungi
- Mosses, Ferns, and Flowering Plants
Lekin isse problems hui:
- Bacteria aur blue-green algae prokaryotic hain, baaki eukaryotic hain
- Fungi heterotrophic hain aur chitin wall rakhte hain, unlike green plants jo autotrophic hain aur cellulose wall rakhte hain
- Chlamydomonas (unicellular) aur Spirogyra (multicellular) dono ko Algae me place kiya gaya, major differences ko ignore karte hue
🌐 Nayi Classification ki zaroorat kyun thi
Whittaker ka system in errors ko correct karta hai by:
- Prokaryotes ko Monera me separate karna
- Unicellular eukaryotes ko Protista ke under group karna
- Fungi ke liye ek separate kingdom create karna unki distinct nutrition aur cell wall ke karan
📚 Modern Developments – Three Domain System
Monera ko do domains me divide kiya gaya:
- Monera was divided into two domains:
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Baaki kingdoms (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia) ko third domain me place kiya gaya: Eukarya
You will study this system in detail in higher classes.
✅ Conclusion
R.H. Whittaker ki Five Kingdom Classification ne organisms ko group karne ka zyada accurate aur evolutionary-based tareeka provide kiya. Yeh older systems ke comparison me ek bada improvement tha kyunki:
- Cell type, body organization, nutrition, aur evolutionary relationships ko consider kiya
- Fungi, bacteria, algae, aur protozoa jaise organisms ko place karne me confusion solve kiya
- Modern taxonomy aur phylogeny ke liye foundation rakha
Jaise-jaise hamari knowledge increase hogi, classification systems future me bhi evolve karte rahenge.
2. Kingdom Monera – Characteristics of Bacteria
Kingdom Monera me sirf ek major group of organisms – bacteria shamil hain. Yeh Earth par sabse simple aur sabse ancient life forms hain, lekin yeh sabse zyada adaptable aur diverse bhi hain.
🌍 Habitat – Where Are Bacteria Found ?
Bacteria har jagah paye jaate hain – yeh Earth ke sabse zyada abundant microorganisms hain..
- Ek handful soil me hundreds of bacteria ho sakte hain.
- Yeh extreme environments me rehe sakte hain, jaise :
- Hot springs
- Deserts
- Snow-covered regions
- Deep oceans
- Kuch bacteria dusre living organisms ke upar ya andar parasites ke roop me live karte hain..
🔬 Types of Bacteria Based on Shape
Bacteria ko unke shape ke basis par char main types me group kiya jaata hai:
| Shape | Name | Plural Form |
|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Coccus | Cocci |
| Rod-shaped | Bacillus | Bacilli |
| Comma-shaped | Vibrio | Vibrio |
| Spiral-shaped | Spirillum | Spirilla |
Yeh classification scientists ko bacteria ko zyada efficiently identify aur study karne me help karta hai.
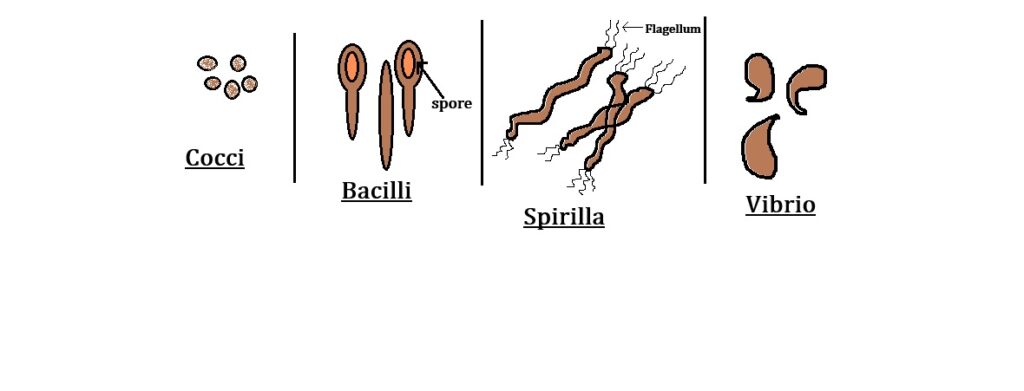
🧪 Structure vs Behaviour
Jabki bacteria ka cell structure bahut simple hai (koi true nucleus ya membrane-bound organelles nahi), unka behavior complex aur advanced hai.
Woh metabolism me huge diversity display karte hain, jo unhe sabse zyada biochemically versatile organisms me se ek banata hai.
🍽️ Nutrition in Bacteria
Bacteria ko iske basis par classify kiya ja sakta hai ki woh food kaise obtain karte hain:
🔹 Autotrophic Bacteria – Make their own food
- Inorganic substances ka use karke food prepare karna
- Two types:
- Photosynthetic autotrophs – use sunlight (e.g., cyanobacteria)
- Chemosynthetic autotrophs – use chemical reactions (e.g., nitrifying bacteria)
🔹 Heterotrophic Bacteria – Depend on others for food
- Zyada tar bacteria is category me fall karte hain.
- They get nutrition from:
- Dead organic matter (saprophytic)
- Living hosts (parasitic)
✅ Conclusion
Kingdom Monera, jo bacteria se consist karta hai, Earth ke sabse widespread aur adaptable organisms me se kuch ko include karta hai.
Yeh:
- Extreme environments me live karte hain
- Various shapes me exist karte hain
- Simple structure rakhte hain lekin complex metabolic activity dikhate hain
- Diverse modes of nutrition show karte hain, dono autotrophic aur heterotrophic
Unki incredible metabolic diversity bacteria ko ecosystems aur human life ke liye vital banati hai.
Kingdom Monera has of two Types- Archaebacteria and Eubacteria.
Archaebacteria – Ancient Survivors of Extreme Environments
Archaebacteria ek unique aur ancient group of bacteria hain jo Kingdom Monera me belong karte hain. Yeh Earth ke sabse extreme aur harsh environments me live karne ke liye jaane jaate hain—aise places jahan zyada tar other life forms survive nahi kar sakte. Unke habitats ke basis par, archaebacteria ko teen major types me classify kiya gaya hai:
- Halophiles – extremely salty environments me paye jaate hain, jaise salt lakes
- Thermoacidophiles – hot springs me survive karte hain jahan very high temperatures aur acidic conditions hoti hain
- Methanogens – oxygen-free, swampy ya marshy areas me live karte hain, jaise ruminants (e.g., cows aur buffaloes) ke digestive tracts
Archaebacteria itni extreme conditions me survive kar sakte hain kyunki unka special cell wall structure dusre bacteria se bahut different hai. Yeh unique composition unhe high salt levels, acidity, aur heat se protect karta hai, jisse yeh extremely resistant aur adaptable ban jaate hain.
Archaebacteria ke sabse important types me se ek methanogens hain, jo biogas production me crucial role play karte hain. Yeh bacteria ruminant animals jaise cows aur buffaloes ke intestines me live karte hain, jahan yeh gut me organic matter ka breakdown karne me help karte hain aur byproduct ke roop me methane gas release karte hain. Yeh methane phir collect karke biogas ke roop me use kiya jaata hai, jo ek renewable source of energy hai, especially rural areas me.
✅ Conclusion
Archaebacteria primitive, microscopic organisms hain jo extreme environments me survive karne ke liye apni specialized cell wall structure ke through adapt kiye hain.
- Yeh halophiles, thermoacidophiles, aur methanogens ko include karte hain
- Methanogens animal dung se methane (biogas) produce karne me especially useful hain
- Simple structure hone ke bawajood, yeh vital ecological aur environmental role play karte hain
- Yeh ancient microbes dikhate hain ki life kaise harshest conditions me bhi adapt aur thrive kar sakti hai Earth par.
Eubacteria – The True Bacteria with Diverse Roles and Forms
ubacteria, jise true bacteria bhi kaha jaata hai, nature me paye jaane wale sabse widespread aur diverse groups of microorganisms me se ek hain. Yeh Kingdom Monera me belong karte hain aur thousands of different forms me exist karte hain. Yeh bacteria apni rigid cell wall ke liye recognized hote hain, aur inme se kai ke paas flagellum bhi hota hai jo unhe move karne me help karta hai (motile bacteria).
🌱 Photosynthetic Autotrophs – Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae)
Eubacteria ka ek important group cyanobacteria hai, jo commonly blue-green algae ke naam se jaana jaata hai. Yeh photosynthetic autotrophs hain, matlab yeh apna khud ka food sunlight ka use karke produce karte hain, bilkul green plants ki tarah. Inme chlorophyll-a hota hai, jo wahi pigment hai jo higher plants photosynthesis ke liye use karte hain.
Cyanobacteria ho sakte hain:
- Unicellular, colonial, ya filamentous
- Freshwater, marine, ya terrestrial environments me found
- Colonies me gelatinous sheath se surrounded
Yeh aksar polluted water bodies me blooms form karte hain, water surface par thick layers create karte hain. Kuch cyanobacteria jaise Nostoc aur Anabaena ke paas specialized cells hote hain jise heterocysts kehte hain, jo atmospheric nitrogen ko fix kar sakte hain – yeh ek bahut important ecological function hai.
⚗️ Chemosynthetic Autotrophic Bacteria
Yeh bacteria sunlight ka use nahi karte lekin energy derive karte hain by oxidizing inorganic substances jaise:
- Ammonia
- Nitrites
- Nitrates
Release hui energy ka use ATP produce karne ke liye hota hai, jo cell ka energy currency hai. Yeh bacteria nutrient recycling me major role play karte hain, especially elements jaise:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Iron
- Sulphur
🍽️ Heterotrophic Bacteria – Decomposers and Pathogens
Zyada tar eubacteria heterotrophs hain, matlab yeh apna food ke liye dusre organisms ya organic matter par depend karte hain. Yeh:
- Nature me sabse zyada abundant bacteria hain
- Dead plants aur animals ko break down karke important decomposers ke roop me kaam karte hain
- Human life me key roles play karte hain, jaise:
- Milk se curd banana
- Producing antibiotics
- Legume roots me nitrogen fix karna (e.g., Rhizobium)
Lekin, sab friendly nahi hote. Kuch heterotrophic bacteria pathogens hote hain, jo humans, plants, aur animals me diseases cause karte hain. Common bacterial diseases me shamil hain:
- Cholera
- Typhoid
- Tetanus
- Citrus canker (crops ko affect karta hai)
🔁 Reproduction in Eubacteria
Eubacteria mainly reproduce karte hain:
- Binary fission – ek simple, asexual method of cell division
- Unfavourable conditions me, survival ke liye spores form karte hain
- Yeh ek primitive form of sexual reproduction bhi perform kar sakte hain, DNA transfer ke through ek bacterium se doosre me (koi gamete formation nahi)
🦠 Mycoplasma – Exception Among Bacteria
Eubacteria se related ek special group hai Mycoplasma:
- Inme cell wall completely lack hoti hai
- Yeh sabse chhote living cells ke roop me known hain
- Oxygen ke bina bhi survive kar sakte hain
- Kai mycoplasmas animals aur plants dono ke liye pathogenic hote hain
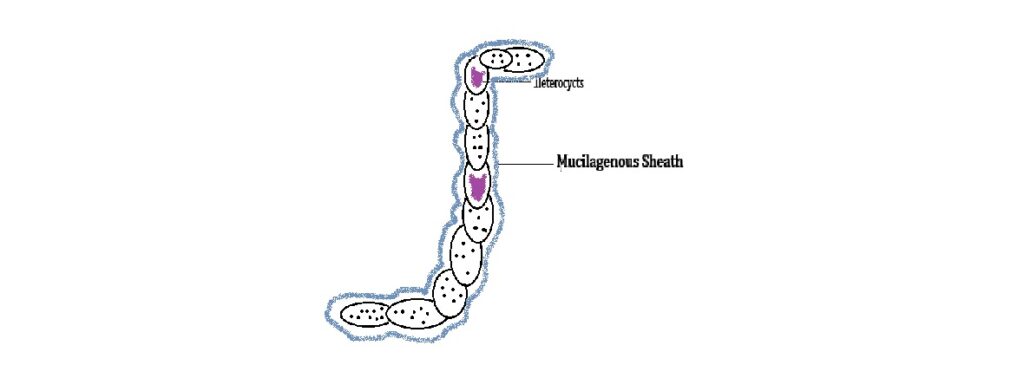
✅ Conclusion
Eubacteria, ya true bacteria, bahut versatile aur essential organisms hain jo ecosystems aur human life ko kai tariko se impact karte hain.
- Yeh photosynthetic cyanobacteria, nutrient-recycling chemosynthetic bacteria, aur food production aur medicine me involved useful heterotrophs ko include karte hain
- Saath hi, yeh harmful pathogens ko bhi include karte hain
- Inka simple structure variety of reproduction methods ko support karta hai, jisse yeh adapt aur survive kar sakte hain
- Inke saath, mycoplasma hume life ki diversity yaad dilate hain, jo cell walls ya oxygen ke bina bhi survive karte hain
3. Kingdom Protista
Kingdom Protista me sabhi single-celled eukaryotic organisms shamil hain. Matlab, yeh organisms sirf ek cell rakhte hain, lekin woh cell advanced hai – isme proper nucleus aur membrane-bound organelles (jaise mitochondria, etc.) hote hain.
Protists mostly water (aquatic environment) me live karte hain. Kuch plant jaise dikhte hain, kuch animal jaise, aur kuch fungi jaise – isliye yeh kingdom plants, animals, aur fungi ke beech ek link mana jaata hai. Scientists kabhi-kabhi decide karne me mushkil face karte hain ki ek organism ko protist, plant, ya kuch aur kaha jaaye.
Kuch protists cilia (small hair-like structures) ya flagella (tail-like structures) ki help se move kar sakte hain.
Yeh organisms do tarike se reproduce kar sakte hain:
- Asexually – simple cell division ke through
- Sexually – do cells ke fusion se zygote banane ke liye
Important groups jo Protista me shamil hain:
- Chrysophytes
- Dinoflagellates
- Euglenoids
- Slime Moulds
- Protozoans
Inme se har group ke different features hote hain. Kuch plant-like (photosynthetic) hain, kuch animal-like (move aur eat kar sakte hain), aur kuch fungi-like behave karte hain.
Introduction to Chrysophytes
Chrysophytes microscopic aquatic organisms ka ek group hain, jo diatoms aur golden algae (jo desmids ke naam se bhi jaane jaate hain) ko include karte hain. Yeh freshwater aur marine water environments dono me live karte hain. Zyada tar freely water me float karte hain aur plankton ka part hote hain. Being photosynthetic, yeh sunlight ka use karke apna khud ka food make karte hain, jo aquatic food chain ke liye important hai.
Diatoms ka unique cell wall silica se bana hota hai, jo glass-like substance hai. Unki walls do overlapping parts se bani hoti hain (jaise soap box ke saath lid). Yeh silica wall bahut hard aur indestructible hai, isliye jab diatoms marte hain, unki walls decay nahi hoti. Billion saalon me, unki cell walls ke remains oceans aur water bodies ke bottom me collect ho gaye hain, aur ek special type ka soft rock form kiya, jise diatomaceous earth kehte hain.
Yeh diatomaceous earth daily life me kaafi useful hai. Kyunki yeh rough aur gritty hai, isse use kiya jaata hai:
- Surfaces polish karne ke liye
- Oils aur syrups filter karne ke liye
- Industrial filters banane ke liye
Saath hi, diatoms oceans ke main producers maane jaate hain, matlab yeh dusre sea organisms ke liye large amount of oxygen aur organic material create karte hain. Yeh aquatic ecosystems me life maintain karne me bahut important role play karte hain.
Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates mostly marine organisms hain aur photosynthesis perform karte hain. Unke cells me pigments ke basis par yeh yellow, green, brown, blue, ya red dikh sakte hain. Unki outer cell wall stiff cellulose plates se bani hoti hai. Inke paas do flagella (tail-like structures movement ke liye) hote hain — ek cell ke length ke along (longitudinal), aur doosra cell ke around groove me (transverse).
Kuch red-colored dinoflagellates, jaise Gonyaulax, itni tezi se multiply karte hain ki sea red dikhne lagta hai — ise red tide kehte hain. Red tides ke dauran release hui toxins harmful ho sakti hain aur nearby fishes ya doosre marine animals ko kill kar sakti hain.
Euglenoids
Euglenoids mostly fresh aur stagnant water me found hote hain. Dusre protists ke unlike, inke paas cell wall nahi hoti. Iske bajay, unka body ek protein-rich flexible layer, pellicle, se covered hota hai, jo unhe shape change karne ki allow karta hai. Inke paas movement ke liye do flagella hote hain — ek short aur doosra long.
Euglenoids dual-natured hote hain. Sunlight me yeh plants ki tarah act karte hain aur photosynthesis perform karte hain. Lekin jab light available nahi hoti, yeh animals ki tarah act karte hain aur chhote organisms par feed karte hain (heterotrophic mode). Inke pigments wahi hote hain jo higher plants me bhi paye jaate hain.
Example: Euglena
Slime Moulds
Yeh saprophytic protists hain, matlab yeh dead aur decaying organic matter par feed karte hain. Inka body slowly rotten leaves aur twigs ke upar move karta hai, nutrients absorb karte hue. Jab conditions favorable hoti hain, yeh ek large, multinucleate, creeping mass form karte hain jise plasmodium kehte hain, jo large area me spread ho sakta hai.
Harsh ya unfavorable conditions me, yeh plasmodium fruiting bodies me change ho jaata hai jo spores produce karte hain. In spores ke paas true protective wall hoti hai, jo unhe bahut strong aur resistant banati hai. Yeh tough environments me bhi kai saalon tak survive kar sakte hain. Spores air currents ke through carry aur spread hote hain.
Protozoans
Protozoans heterotrophic unicellular protists hain jo ya to free-living predators ke roop me ya parasites ke roop me live karte hain. Yeh animals ke sabse primitive relatives consider kiye jaate hain. Inke movement aur mode of life ke basis par, protozoans ko char main groups me divide kiya gaya hai.
- Amoeboid protozoans fresh water, sea water, ya moist soil me live karte hain. Yeh pseudopodia (false feet) ka use karke move aur feed karte hain, bilkul Amoeba ki tarah. Kuch marine types ke surface par silica shells hote hain, jabki parasitic forms jaise Entamoeba dusre organisms ke andar live kar sakte hain.
- Flagellated protozoans free-living ya parasitic ho sakte hain aur movement ke liye ek ya zyada flagella rakhte hain. Kuch parasitic forms diseases cause karte hain, jaise sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma).
- Ciliated protozoans aquatic hote hain aur numerous tiny cilia se covered hote hain. Yeh cilia unhe move karne me help karte hain aur food ko ek special cavity me direct karte hain, jise gullet kehte hain. Paramecium is group ka common example hai.
- Sporozoans protozoans ka ek group hai jinke paas movement ke liye special structures nahi hote. Inke life cycle me ek infectious spore-like stage hoti hai. Sabse well-known example Plasmodium hai, jo malaria cause karta hai, ek serious disease jo globally millions of logon ko affect karti hai.
4. Kingdom Fungi
Fungi ek separate group of living organisms hain jo heterotrophic hain, matlab yeh apna khud ka food nahi bana sakte aur dusron par depend karte hain. Yeh shape (morphology) aur habitat me kaafi variation dikhate hain. Aapne fungi ko moist bread ya spoiled fruits par grow karte dekha hoga. Hum jo mushrooms khate hain aur toadstools bhi fungi ke types hain. Kabhi-kabhi mustard leaves par white patches ek fungus ke karan hote hain, jo plants par parasite ke roop me live karta hai.
Kuch fungi humare liye useful hote hain. Jaise, yeast ek unicellular fungus hai jo bread aur beer banane me use hota hai. Dusri taraf, kuch fungi diseases cause karte hain. Ek important example Puccinia, jo wheat me rust disease cause karta hai. Kuch fungi antibiotics banane me bhi help karte hain. Penicillium ek fungus hai jo hume antibiotic penicillin deta hai. Fungi almost har jagah found hote hain – air, water, soil, aur living plants aur animals par. Yeh mostly warm aur moist (humid) places me grow karte hain, isliye hum food refrigerator me rakhte hain – fungal ya bacterial spoilage ko prevent karne ke liye.
Zyada tar fungi, yeast ke alawa, ka body fine, thread-like structures hyphae se bana hota hai. In threads ka bada group mycelium kehlaata hai. Kuch fungi me hyphae me divisions nahi hote aur ek single large cell me multiple nuclei hote hain – inhe coenocytic hyphae kehte hain. Dusre fungi me hyphae septa (cross-walls) se divide hote hain. Fungal cells ka outer wall chitin aur complex sugars (polysaccharides) se bana hota hai.
Fungi heterotrophic hote hain, matlab yeh apna food dusre sources se lete hain. Kuch fungi dead aur decaying matter par feed karte hain – inhe saprophytes kehte hain. Kuch fungi living organisms par live karke unhe harm karte hain – inhe parasites kehte hain. Kuch fungi aise organisms ke saath close partnership me live karte hain jahan dono partners ko benefit hota hai – inhe symbionts kehte hain. Jaise, fungi algae ke saath lichens banate hain aur higher plant roots ke saath mycorrhiza banate hain.
Fungi teen tariko se reproduce karte hain: vegetative, asexual, aur sexual reproduction. Vegetative reproduction me fungi fragments me break hoke, fission (splitting) ya budding (naya cell purane se form) karke reproduce karte hain. Asexual reproduction me yeh spores produce karte hain jaise conidia, sporangiospores, ya zoospores. Yeh spores special structures fruiting bodies ke andar form hote hain.
Fungi me sexual reproduction teen main steps me hoti hai. Pehla hai plasmogamy, jahan do parent cells (gametes) ka cytoplasm fuse hota hai. Next hai karyogamy, jahan nuclei fuse karke single nucleus banate hain. Phir meiosis hoti hai, jisse haploid spores form hote hain. Kai fungi jaise ascomycetes aur basidiomycetes me plasmogamy aur karyogamy ke beech ek special stage hoti hai, dikaryophase. Is stage me har cell me do separate nuclei (n + n) hote hain. Baad me nuclei fuse hoke diploid cell (2n) bante hain, aur phir meiosis se haploid spores form hote hain.
Fungi ko different groups me classify kiya jaata hai based on unka mycelium kaisa dikhta hai, spores kaise form hote hain, aur kis type ke fruiting bodies produce hote hain. Yeh features scientists ko fungi ko kingdom Fungi ke under various classes me divide karne me help karte hain.
Phycomycetes – Class of Fungi
Members of the group Phycomycetes mostly wet ya moist environments me found hote hain. Yeh usually aquatic places, rotting wood, ya damp soil me grow karte hain. Kuch members obligate parasites ke roop me plants par live karte hain, matlab survival aur reproduction ke liye unhe living host par rehna zaroori hota hai.
In fungi ka body mycelium se bana hota hai, jo aseptate (cross walls nahi hote) aur coenocytic (ek single large cell me kai nuclei hote hain) hota hai. Is tarah ka structure fungus ko quickly grow aur easily spread karne ki allow karta hai.
Reproduction phycomycetes me dono asexual aur sexual ways se hoti hai. Asexual reproduction me yeh zoospores (jo flagella ki help se move karte hain) ya aplanospores (non-motile) produce karte hain. Yeh spores ek structure, sporangium, ke andar form hote hain aur internally (endogenously) develop hote hain.
Sexual reproduction me, yeh fungi do gametes ke fusion se thick-walled zygospore form karte hain. Ye gametes ya to same dikhte hain (isogamous) ya shape/size me different hote hain (anisogamous ya oogamous). Is type ka fusion next generation me genetic variation ensure karta hai.
Kuch commonly known examples of phycomycetes:
- Mucor – decaying organic matter par found
- Rhizopus – commonly known as bread mould
- Albugo – parasitic fungus jo mustard plants ko infect karta hai
Ascomycetes – Class of Fungi
Ascomycetes fungi ka ek group hai jo commonly sac fungi ke naam se jaane jaate hain, kyunki inke sexual spores ek sac-like structure ke andar form hote hain. Zyada tar ascomycetes multicellular hote hain, jaise Penicillium, lekin kuch unicellular hote hain, jaise yeast (Saccharomyces).
Yeh fungi alag-alag tariko se live kar sakte hain. Kuch saprophytic hote hain (dead matter par feed karte hain), kuch decomposers ki tarah act karte hain, kuch parasitic hote hain (living organisms par live karke harm karte hain), aur kuch coprophilous hote hain, matlab animal dung par grow karte hain.
Ascomycetes ka body branched aur septate mycelium se bana hota hai, matlab hyphae cells me cross-walls se divide hote hain. Asexual reproduction me yeh spores produce karte hain, jise conidia kehte hain. Yeh conidia outside (exogenously) special structures conidiophores par form hote hain. Conidia ke germinate hone par naya mycelium grow karta hai.
Sexual reproduction me, yeh spores produce karte hain, jise ascospores kehte hain. Yeh spores inside (endogenously) sac-like structure ascus (plural: asci) me bante hain. Asci grouped hoke special structures ascocarps form karte hain, jo ascomycetes ke fruiting bodies ka kaam karte hain.
Kuch commonly known examples of ascomycetes:
- Aspergillus – ek mold jo food par grow karke spoilage cause karta hai
- Claviceps – ek plant disease ergot ke liye jaana jaata hai
- Neurospora – genetic aur biochemical research me widely use hota hai
- Kai ascomycetes jaise morels aur truffles edible hote hain aur world ke kai parts me luxury food ya delicacies ke roop me consider kiye jaate hain
Basidiomycetes – Class of Fungi
Basidiomycetes fungi ka ek group hai jo kai commonly known forms include karte hain jaise mushrooms, bracket fungi, aur puffballs. Yeh fungi usually soil, rotting wood logs, tree stumps, ya living plants ke andar parasites ke roop me grow karte hain. Parasitic members me rusts aur smuts shamil hain, jo crops me diseases cause karte hain.
Basidiomycetes ka body branched aur septate mycelium se bana hota hai, matlab unke hyphae cross-walls se compartments me divide hote hain. Zyada cases me asexual spores nahi bante, lekin yeh vegetatively reproduce kar sakte hain fragmentation ke through — jahan fungus ka ek piece break off karke naya organism grow karta hai.
Basidiomycetes ke distinct sex organs nahi hote. Sexual reproduction plasmogamy se begin hoti hai, jo do different vegetative ya somatic cells (different strains ya types) ke cytoplasm ka fusion hai. Is fusion se dikaryotic structure form hota hai, jahan har cell me do nuclei (n + n) hote hain.
Yeh dikaryotic stage eventually basidium (plural: basidia) form karta hai, jahan sexual reproduction ke final steps hote hain. Basidium me do nuclei fuse hoke (karyogamy), phir meiosis hoti hai, aur char haploid spores form hote hain, jise basidiospores kehte hain. Yeh basidiospores outside (exogenously) basidium par form hote hain.
Basidia grouped hoke special structures basidiocarps form karte hain, jo basidiomycetes ke fruiting bodies hote hain.
Kuch common examples of basidiomycetes:
- Agaricus – common edible mushroom
- Ustilago – crops me smut disease cause karta hai
- Puccinia – wheat me rust disease ke liye responsible hai
Deuteromycetes – Class of Fungi
Deuteromycetes commonly imperfect fungi ke naam se jaane jaate hain, kyunki is group me sirf fungi ke asexual ya vegetative phases hi known hote hain. Inka sexual reproduction stage ya to observe nahi kiya gaya hota hai ya clearly identify nahi hota. Isliye inhe “imperfect” kaha jaata hai.
Kai cases me, jab kisi fungus ka sexual stage baad me discover hota hai, to fungus ko uske correct group me move kar diya jaata hai, usually Ascomycetes ya Basidiomycetes, unke characteristics ke hisaab se. Kabhi-kabhi wahi fungus do alag-alag names bhi rakh sakta hai – ek asexual stage ke liye (Deuteromycetes me classified) aur ek sexual stage ke liye (dusre group me classified). Jab scientists dono stages ke beech connection figure out kar lete hain, to fungus ko correctly reclassified kar diya jaata hai aur ab woh Deuteromycetes ka part nahi mana jaata.
Deuteromycetes sirf asexual spores ke through reproduce karte hain, jise conidia kehte hain. Yeh spores naye fungal colonies ko spread aur grow karne me help karte hain. In fungi ka body branched aur septate mycelium se bana hota hai, matlab hyphae cross-walls se divide hote hain.
Is group ke members alag-alag modes of living dikhate hain. Kuch saprophytes hote hain, matlab dead aur decaying matter par live karte hain. Dusre parasites hote hain, jo living organisms par live karke unhe harm karte hain. Zyada tar Deuteromycetes plant litter ke important decomposers hote hain aur minerals ko recycle karne me nature me help karte hain, jisse ye ecological point of view se kaafi important ban jaate hain.
5. Plants Kingdom
Kingdom Plantae me wo saare organisms shamil hote hain jo eukaryotic hote hain (well-defined cells with a nucleus) aur chlorophyll contain karte hain, jo green pigment hai aur photosynthesis me use hota hai. In organisms ko commonly plants kehte hain. Zyada tar plants apna food sunlight ki help se make karte hain, lekin kuch special types partially heterotrophic hote hain — matlab ye doosre organisms par depend karte hain food ke liye.
Aise heterotrophic plants ke examples me insectivorous plants jaise Bladderwort aur Venus flytrap, jo insects ko trap aur digest karte hain, aur parasitic plants jaise Cuscuta (Amarbel) shamil hain, jo doosre plants par grow karke nutrients absorb karte hain.
Plant cells ka typical eukaryotic structure hota hai, matlab inme proper nucleus aur organelles hote hain. Inke cells me chloroplasts bhi hote hain (jahan photosynthesis hoti hai) aur cell wall mainly cellulose se bani hoti hai, jo unhe structure aur strength deti hai.
Plant kingdom me wide range of groups shamil hain jaise:
- Algae
- Bryophytes (mosses aur liverworts)
- Pteridophytes (ferns aur unke relatives)
- Gymnosperms (non-flowering seed plants jaise pine)
- Angiosperms (flowering plants)
Plants ka life cycle ek unique pattern dikhata hai, jise alternation of generations kehte hain. Iska matlab hai ki plants ke do main phases hote hain:
- Diploid Sporophyte Phase (2n) – spores produce karta hai
- Haploid Gametophyte Phase (n) – gametes (sex cells) produce karta hai
Yeh dono phases har plant ke life cycle me ek dusre ke saath alternate karte hain. In phases ki length aur dominance alag-alag plant groups me vary karti hai. Kuch me sporophyte zyada dominant aur long-living hota hai, jabki kuch me gametophyte major role play karta hai.
Is process ko jisme diploid aur haploid stages ek ke baad ek aate hain, alternation of generations kehte hain aur yeh Kingdom Plantae ke saare members ka key feature hai. You Study In Further Chapters🥰.
6. Animalia Kingdom
Kingdom Animalia me wo saare heterotrophic, eukaryotic, aur multicellular organisms shamil hote hain. Inke cells me cell walls nahi hote, jo unhe plants se alag banata hai. Ye organisms directly ya indirectly plants par depend karte hain apna food ke liye. Ye food ko body cavity ke andar digest karte hain aur extra food ko glycogen ya fat ke form me store karte hain.
Inka mode of nutrition holozoic kehlaata hai, matlab ye solid food ko ingest karke digest karte hain. Ye definite growth pattern follow karke grow karte hain aur adult stage me ek specific shape aur size achieve karte hain. Higher animals ke paas advanced sense organs aur nervous systems hote hain, jo unhe surroundings ka respond karne me help karte hain. Zyada tar animals ek jagah se dusri jagah move kar sakte hain (locomotion).
Animals me reproduction usually sexual hoti hai, jahan male aur female organisms copulate karte hain aur ek zygote form hota hai, jo phir embryological stages ke through ek naya individual develop karta hai.
7.Viruses, Viroids, Prions, and Lichens – Simple Notes for NEET
Whittaker ke five-kingdom classification me kuch organisms jaise viruses, viroids, prions, aur lichens include nahi kiye gaye. Ye organisms nature me unique hain aur inhe neeche briefly discuss kiya gaya hai.

Viruses
Viruses ko truly living organisms nahi maana jaata kyunki inme cellular structure nahi hota. Ek host cell ke bahar, viruses non-living, crystalline particles ke roop me exist karte hain. Lekin, jab ye ek living cell me enter karte hain, ye active ho jaate hain, cell ke machinery ko control karte hain, aur replicate karte hain, aksar host cell ko mar dete hain. Isse ye sawaal uthta hai: viruses living hain ya non-living?
Virus shabd ka matlab hai poison. 1892 me, Dmitri Ivanowsky ne paaya ki tobacco plants me ek disease (mosaic disease) kuch aisa se hota hai jo bacteria se chhota hai. Baad me 1898 me, M.W. Beijerinck ne isse confirm kiya aur is infectious fluid ko Contagium vivum fluidum (infectious living fluid) kaha. 1935 me, W.M. Stanley ne dikhaya ki viruses crystallize ho sakte hain, jo confirm karta hai ki ye host ke bahar non-living hote hain.
Viruses ka structure protein coat (capsid) aur genetic material se bana hota hai, jo ya to DNA ya RNA ho sakta hai, lekin dono nahi. Capsid chhote units, capsomeres, se bana hota hai, jo helical ya geometric shapes me arranged hote hain.
- Plant viruses usually single-stranded RNA rakhte hain.
- Animal viruses me single- ya double-stranded RNA ya DNA ho sakta hai.
- Bacteriophages (jo bacteria ko infect karte hain) usually double-stranded DNA rakhte hain.
Viruses obligate parasites hote hain, matlab ye host ke bina survive ya reproduce nahi kar sakte. Ye humans me flu, mumps, smallpox, herpes, AIDS jaise diseases cause karte hain, aur plants me mosaic patterns, leaf curl, aur stunted growth create karte hain.
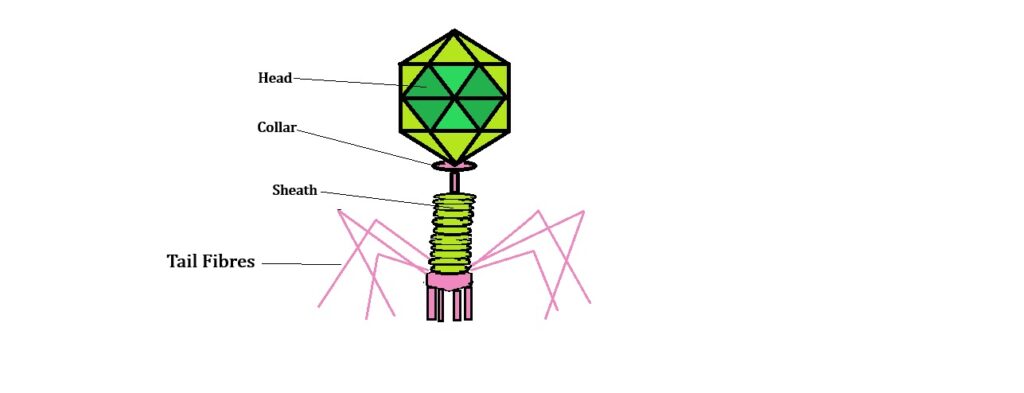
Viroids
Viroids viruses se bhi chhote hote hain aur inhe 1971 me T.O. Diener ne discover kiya. Ye chhote, circular RNA molecules hote hain jo protein coat se free hote hain. Viroids sabse pehle potato spindle tuber disease me paye gaye. Inka RNA low molecular weight ka hota hai, aur viruses ke unlike, viroids me sirf RNA hi hota hai.
Prions
Prions infectious agents hote hain jo sirf abnormally folded proteins se bane hote hain. Inme koi nucleic acids (DNA ya RNA) nahi hote. Prions degenerative neurological disorders cause karte hain. Sabse jaane-mane prion diseases hain:
- Mad cow disease (Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy ya BSE) cattle me
- Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) humans me
Lichens
Lichens ek single organism nahi hote, balki ye ek symbiotic association hote hain ek alga aur ek fungus ke beech.
- Algal part ko phycobiont kehte hain, jo autotrophic hai (photosynthesis se food banata hai).
- Fungal part ko mycobiont kehte hain, jo heterotrophic hai (alga par food ke liye depend karta hai).
Alga food provide karta hai, aur fungus protection, water, aur minerals deta hai. Ye relationship itni close hai ki lichens ek single organism jaise lagte hain. Lichens pollution ke liye bahut sensitive hote hain aur air quality ke excellent indicators hote hain, kyunki ye polluted areas me grow nahi karte.
Thank You 💕By
